The "sense of security" provided by neonatal tracheal intubation training model plays an important role in medical education. Especially in the training process of new medical staff, this training model can bring them great confidence and help them to master the technology and reduce the risk in real operation.
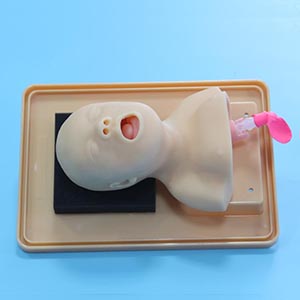
Neonatal Tracheal intubation model
1. The role of teaching models
Teaching models are usually presented in two forms: virtual simulation and physical simulation. The virtual model simulates different intubation scenarios through software and provides participants with real-time feedback to help them understand the various challenges they may encounter during intubation. The physical model simulates the airway of a newborn through highly simulated materials such as silicone and polyurethane, allowing participants to touch realistic airway responses, which is essential to improve the accuracy and confidence of the operation.
This "sense of security" comes from several sources:
- Risk-free operation : Students can practice repeatedly without any risk, reducing mistakes caused by nervousness or unproficiency in actual clinical operation.
- Immediate feedback : Most modern training models can provide immediate feedback, so that students can quickly correct errors when they are found, thereby enhancing operational confidence.
- Simulated environment : Through a highly reproduced simulated environment, students can feel the complexity of airway anatomy and understand how to complete the intubation without causing airway damage.
2. The perspective of industry experts
Industry experts generally believe that model training is not only a tool for skill training, but also a key means to improve the clinical response ability and operational accuracy of medical personnel. Experts stressed that although the training model can provide certain technical guarantees for students, the "security" in operation is not entirely derived from the model itself. It depends more on long-term clinical experience and sensitivity to detail.
For example, some experienced anesthesiologists and pediatricians have mentioned that model training has helped them become more calm in the face of complex situations. But a true sense of safety needs to be built through real-world clinical practices combined with simulated training, especially when dealing with high-risk newborn cases.

3. Data support
In recent years, several studies have shown that simulation training can significantly improve the success rate of novice health care workers during intubation operations. For example, a study of tracheal intubation training in newborns showed a 30 percent increase in intubation success and a 20 percent reduction in operating time among health care workers who received simulated training. This suggests that the "sense of security" provided by the training model through simulation not only improves skill proficiency, but also strengthens the self-confidence of the trainees, thereby improving safety in clinical practice.
Conclusion
The neonatal tracheal intubation training model provides a valuable "sense of security" for healthcare professionals, especially in situations where skills are unskilled or clinical experience is insufficient. Although model training alone cannot completely replace clinical experience, it is undoubtedly an important tool for improving operational accuracy and reducing medical errors. As the technology continues to evolve, future models may become more accurate and realistic, better providing safety and confidence to medical personnel.
